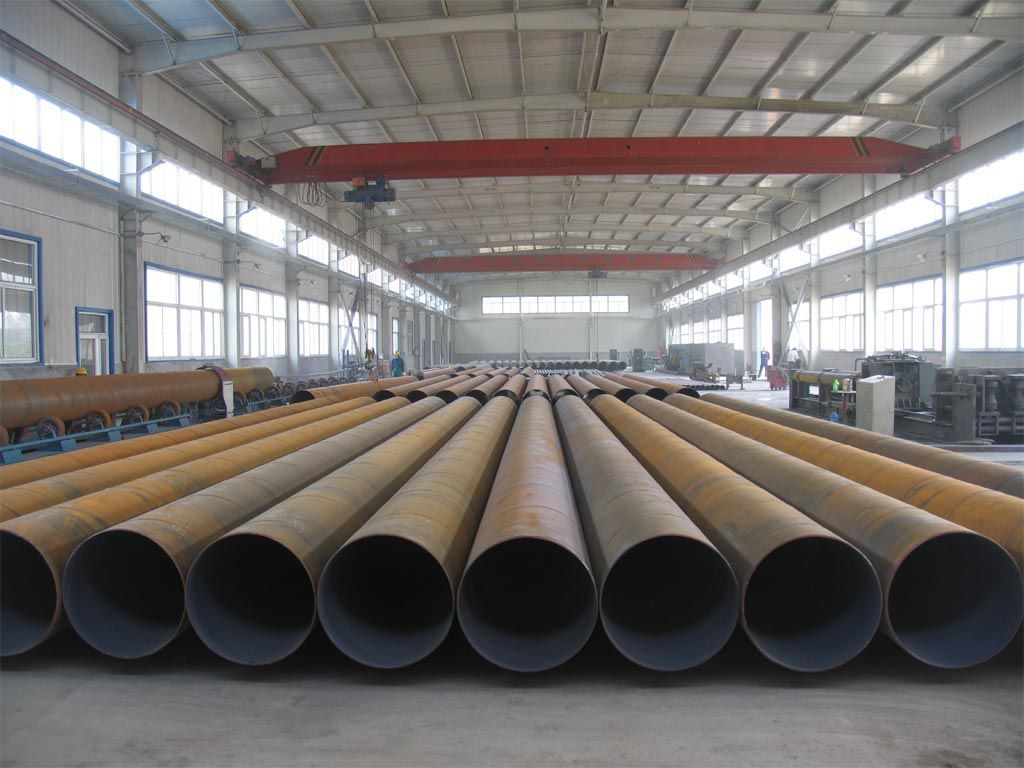
Welded steel pipes are manufactured by rolling steel plates or coils into cylindrical shapes and joining the edges through various welding techniques, including high-frequency induction welding (HFIW), submerged arc welding (SAW), and electric resistance welding (ERW). These pipes are widely used in construction, infrastructure, and industrial applications due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility.
CREDIT
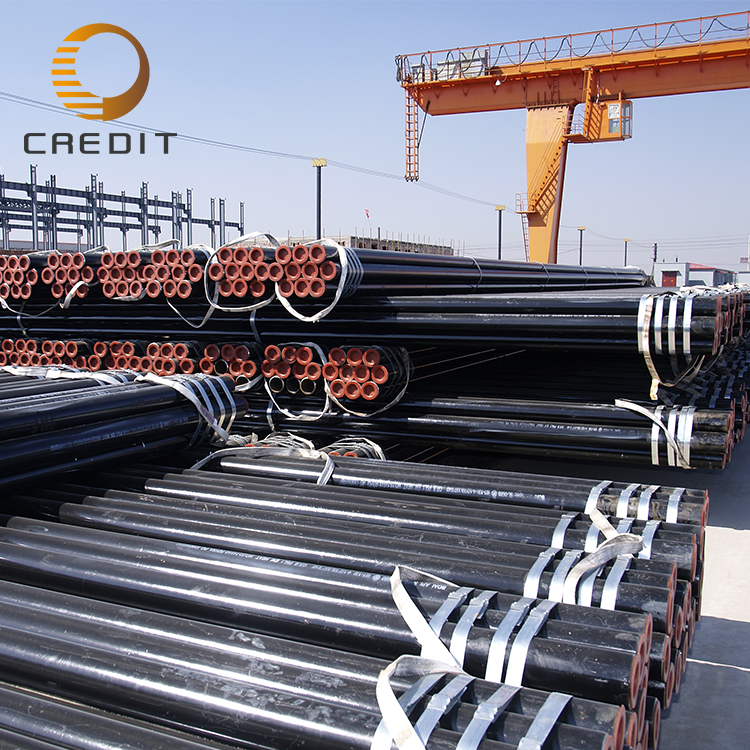

Common specifications include diameters ranging from 10mm to 2,000mm, with wall thicknesses between 1mm to 25mm, available in standard lengths of 6-12 meters. Welded pipes are extensively applied in water and gas distribution, structural frameworks, fencing, and low-to-medium-pressure pipelines. Their key advantages include lower production costs, high manufacturing efficiency, and the ability to produce large diameters.

The global welded pipe market is expanding due to urbanization and infrastructure investments, particularly in emerging economies. Future trends include the adoption of automated welding technologies and high-strength steel grades for improved performance.
Quality control involves material inspection, weld seam testing (ultrasonic or X-ray), and hydrostatic pressure verification to ensure compliance with standards like API, ASTM, and ISO. With continuous advancements in welding technology, welded steel pipes remain a reliable choice for diverse industrial applications.