Rebar, officially known as hot-rolled ribbed steel bar, is a crucial type of construction steel. Produced through the hot-rolling process, it boasts high production efficiency, low cost, and stable performance, making it the primary rebar product on the market. Rebar features spiral ribs, which not only enhance the bond between the steel and concrete but also help distribute stress and improve structural stability.
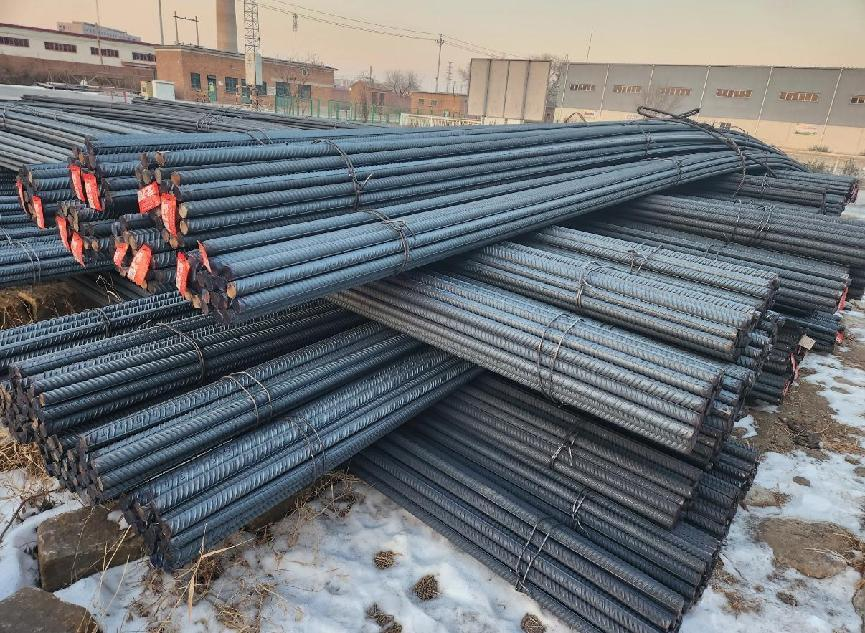

Rebar specifications are mainly distinguished by diameter and rib pattern. Diameters typically range from 6mm to 50mm, with common specifications including 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, 14mm, 16mm, 18mm, 20mm, 22mm, 25mm, 28mm, 32mm, 36mm, and 40mm. Supply lengths are divided into cut-to-length and multiple-length options, usually 9m and 12m. Additionally, rib patterns are mainly classified as standard and high-strength.
Due to its high strength, good ductility, and weldability, rebar has extensive applications in both industrial and construction fields.
· Construction Industry: Rebar is indispensable for infrastructure projects such as houses, bridges, tunnels, and highways. It primarily reinforces concrete structures, such as beams, columns, and floor slabs in buildings, enhancing seismic resistance and stability.
· Manufacturing: In machinery manufacturing, rebar is used to make various mechanical components, such as crane support structures and machine tool bases. In the automotive industry, it's used for vehicle frames and chassis components.
· Energy Sector: Wind power facilities require significant amounts of rebar for tower and foundation structures. The oil and gas industry also uses it for drilling platform and pipeline support structures.

· High Strength: Rebar offers high tensile strength, providing excellent load-bearing capacity, especially suitable for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures.
· Good Plasticity: Rebar can be heat-treated to alter its mechanical and chemical properties, meeting architectural design and development needs.
· Excellent Processability: It exhibits good plasticity and reliability during processing, allowing for various manufacturing techniques to produce different steel shapes.
· Corrosion Resistance: Under certain conditions, rebar provides good corrosion resistance, making it more reliable in complex environments.
· Environmental and Energy Efficiency: As a recyclable building material, rebar complies with environmental requirements during production and use, contributing to the green development of the construction industry.
· Robust Demand and Supply: With the continuous development of infrastructure and the real estate market, the demand for rebar continues to increase. Domestic steel mills are actively expanding production capacity to meet market demand.
· Price Fluctuations: Rebar prices are influenced by various factors, including raw material costs, market supply and demand, and international trade dynamics. In recent years, raw material price hikes and stricter environmental policies have led to fluctuating and upward price trends.
· Green Manufacturing: As the country places greater emphasis on environmental protection, the rebar market will increasingly focus on green production.
· Industry Upgrading: Amid overcapacity, the steel industry faces pressure for industrial upgrading. The rebar market will prioritize product quality and technological innovation to enhance product value-added and market competitiveness.
· International Development: With the deepening of global economic integration, the domestic rebar market will gradually integrate into international markets. Steel mills need to actively expand overseas markets, increasing international market share and brand influence.

The quality inspection process for rebar typically includes the following steps:
· Dimension and Shape Inspection: Measures diameter, length, rib pattern, etc., to ensure products meet specifications.
· Surface Quality Inspection: Checks surface smoothness, flatness, crack-free and rust-free conditions, ensuring good surface quality.
· Composition Testing: Detects the content of elements such as carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphorus, and sulfur, ensuring products comply with national standards.
· Other Tests: May include metallographic analysis, failure analysis, and non-destructive testing to comprehensively assess product quality and performance.
In summary, as a critical type of construction steel, rebar plays a vital role in construction, manufacturing, and energy sectors. With increasing market demand and technological advancements, the rebar market exhibits broad development prospects.