Galvanized Iron Wire: A Versatile Foundation for Building Materials
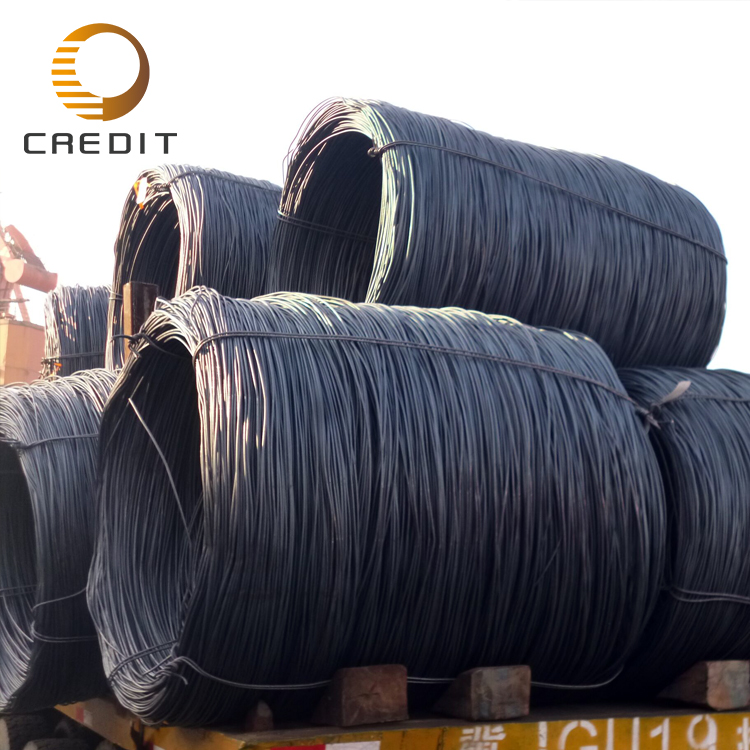

Galvanized iron wireis a metal wire product made by coating the surface of low-carbon steel wire with a layer of zinc. It features excellent corrosion resistance and ductility and is widely used across various industries, especially in building materials, agriculture, industry, and civil applications. Its primary raw material is high-quality low-carbon steel, which undergoes processes such as drawing, acid pickling, high-temperature annealing, and either hot-dip or electro-galvanizing.
Common specifications include diameters ranging from 0.3 mm to 6.0 mm, with surfaces available in bright or matte zinc finishes. Packaging is typically in coils or straight lengths, depending on usage needs. Galvanization methods are divided into electro-galvanized and hot-dip galvanized types, with the latter offering superior corrosion resistance for outdoor or humid environments.
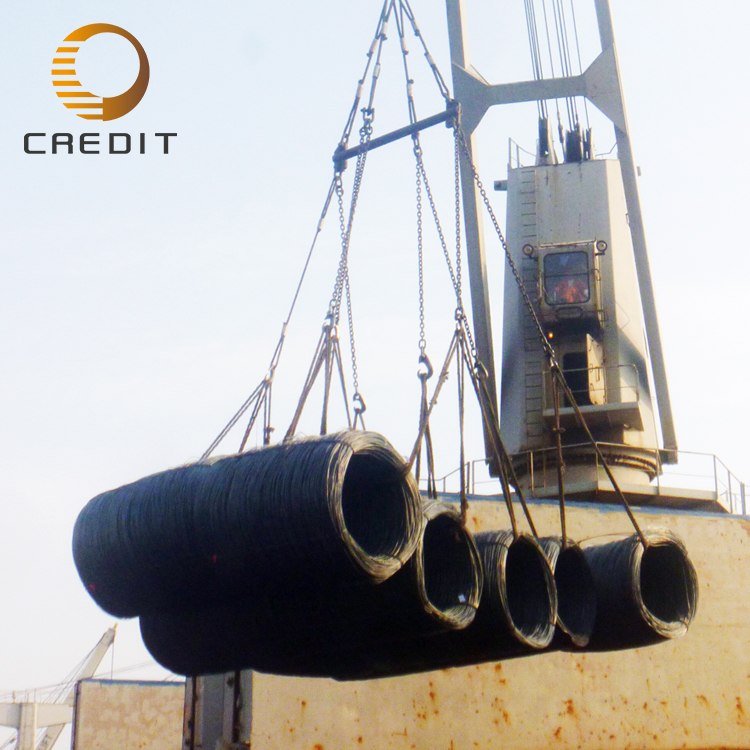

In terms of applications, galvanized iron wire is commonly used to manufacture wire mesh, fencing, rebar tying wire, agricultural enclosures, grapevine trellises, and flower supports. Its excellent flexibility and workability make it easy to bend, weld, and shape, making it ideal for many infrastructure and landscaping projects.
The advantages of this product include strong rust resistance, long service life, low cost, and ease of installation. It performs particularly well in outdoor or coastal environments due to its stability and durability. Compared with ordinary iron wire, galvanization significantly enhances overall performance and lifespan.
As infrastructure development continues and agricultural automation advances, the market for galvanized iron wire is showing steady growth. Environmental protection and sustainability trends are also driving the adoption of lead-free galvanizing and other innovative techniques, helping increase product value and international competitiveness. The future outlook for this industry remains highly promising.
In terms of quality inspection, the process typically involves raw material chemical composition analysis, zinc coating thickness testing, tensile strength and elongation testing, appearance inspection, and packaging integrity checks. These steps ensure that every batch meets national standards or specific customer requirements.
In conclusion, galvanized iron wire, as a traditional yet essential building material, continues to expand its range of applications due to its outstanding properties and versatility, and it is poised for broader development in the future.