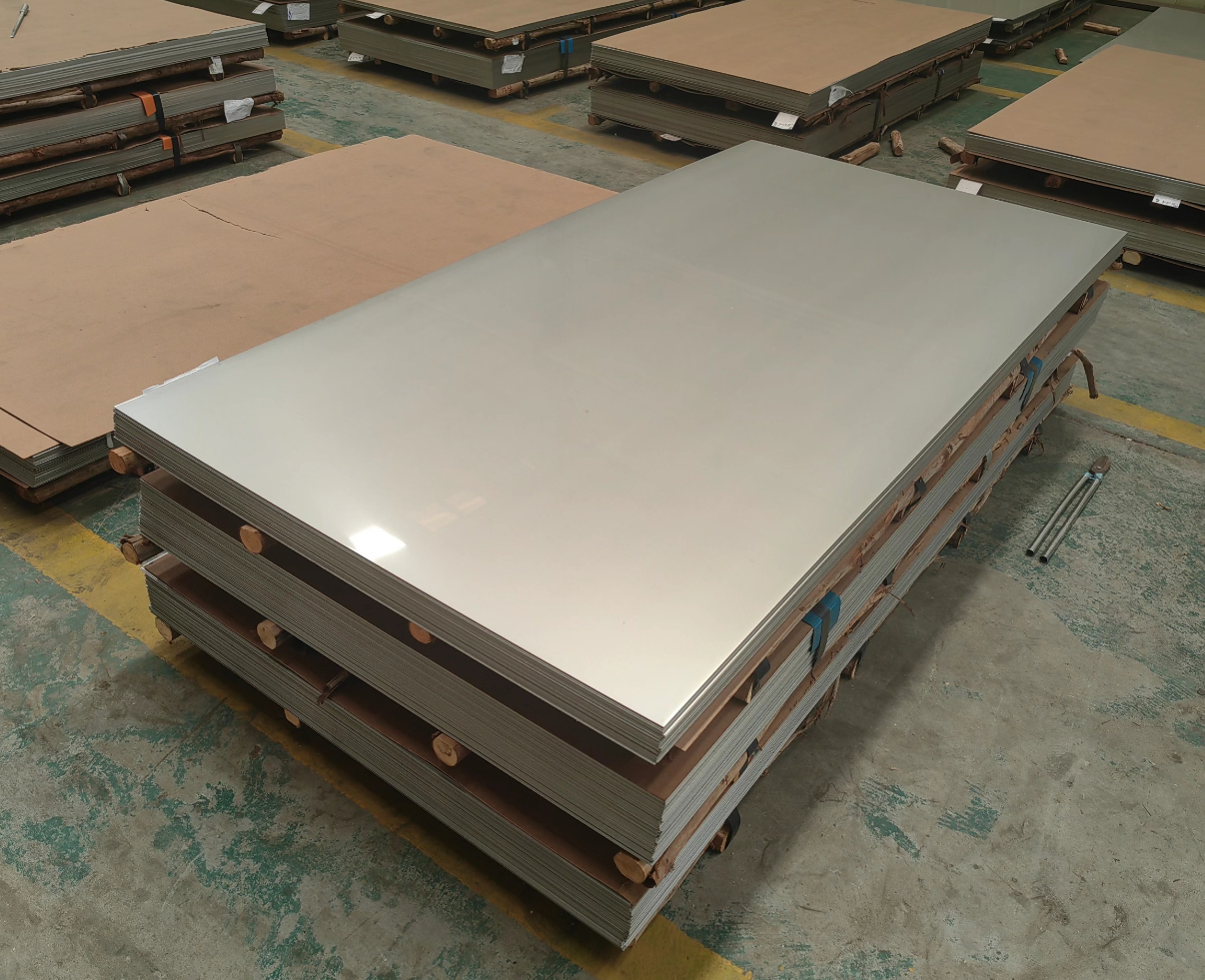
Stainless steel plate generally refers to a collective term for stainless steel plate and acid-resistant steel plate, laying an important material and technological foundation for the development of modern industries and technological advancements. Below is a detailed introduction to stainless steel plate products:
Stainless steel plates come in various specifications based on production processes and applications. Here are some common specifications:
Cold-rolled Stainless Steel Plate:
Common Specifications: 100*200, 122*2440, 122*305, 122*400, 150*300, 150*600, etc.
Thickness Range: 0.3~6.0mm.
CREDIT
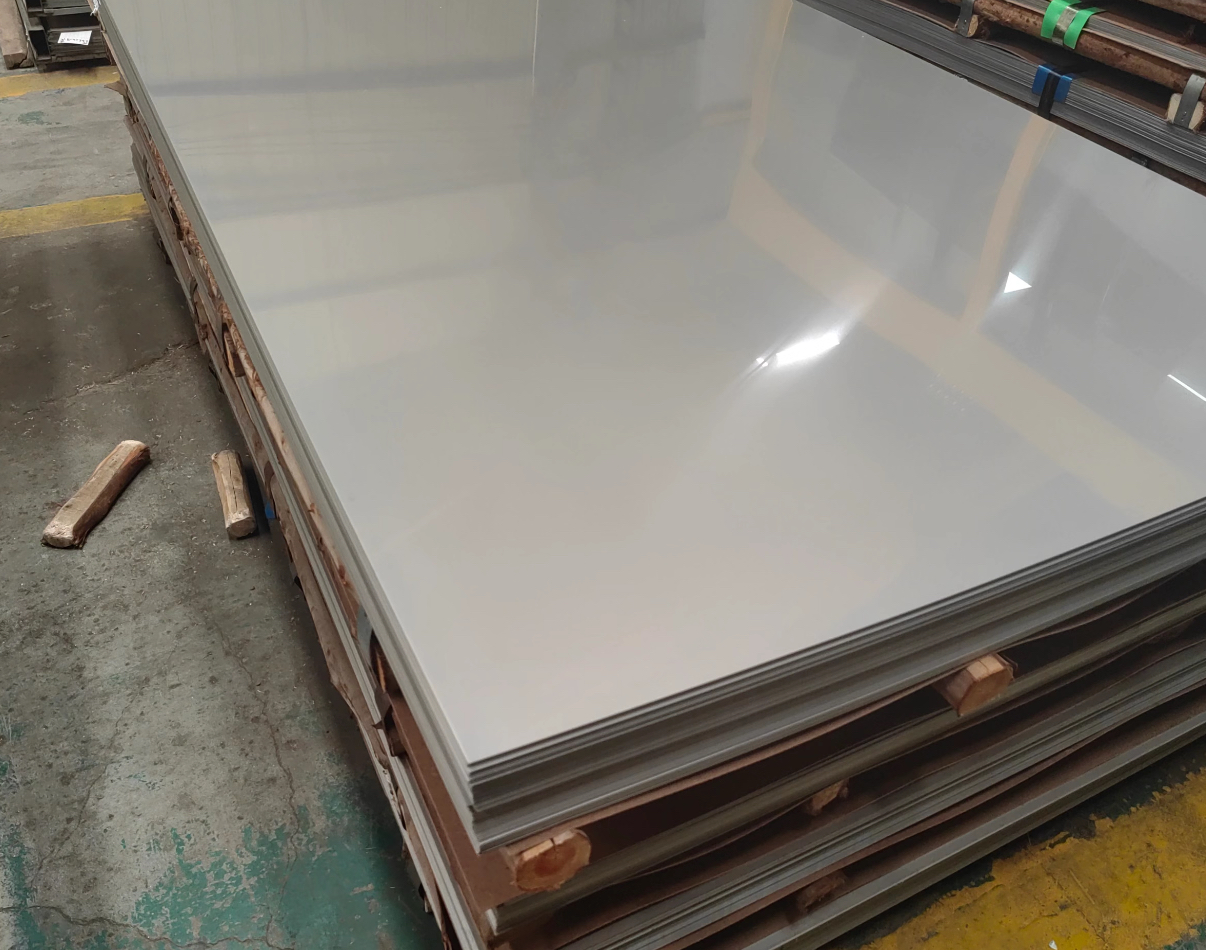

Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, stainless steel plates have a wide range of applications:
Architectural Decoration: Used for exterior walls, curtain walls, ceilings, stairway handrails, doors and windows, etc., due to its aesthetic appearance and weather resistance.
Kitchen Furniture: Used in the manufacture of kitchen furniture, such as kitchen countertop, sinks, and worktables, due to its rust resistance, easy cleaning, and odorless.
Chemical Equipment: Used in the manufacture of chemical equipment, such as heaters, heat exchanger, storage tanks, and filters, due to its corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, and wear resistance.
Food Processing: Widely used in the food processing industry, such as breweries, dairies, and other food factories, to avoid food contamination.
Automobile Manufacturing: Used in the manufacture of automobile parts and components, such as bodies, exhaust pipes, and fuel tanks, due to its excellent strength and corrosion resistance.
Medical Equipment: Used in the manufacture of medical equipment, such as surgical instruments and utensils, due to its antibacterial and easy-to-clean properties.
Shipbuilding: Used in shipbuilding, such as hulls, piping, and equipment supports, due to its resistance to seawater corrosion and wear resistance.
In addition, stainless steel plates are also used in the manufacture of electronic device casings, structural components, various mechanical parts and components, as well as structural parts and components for aircraft and rockets.
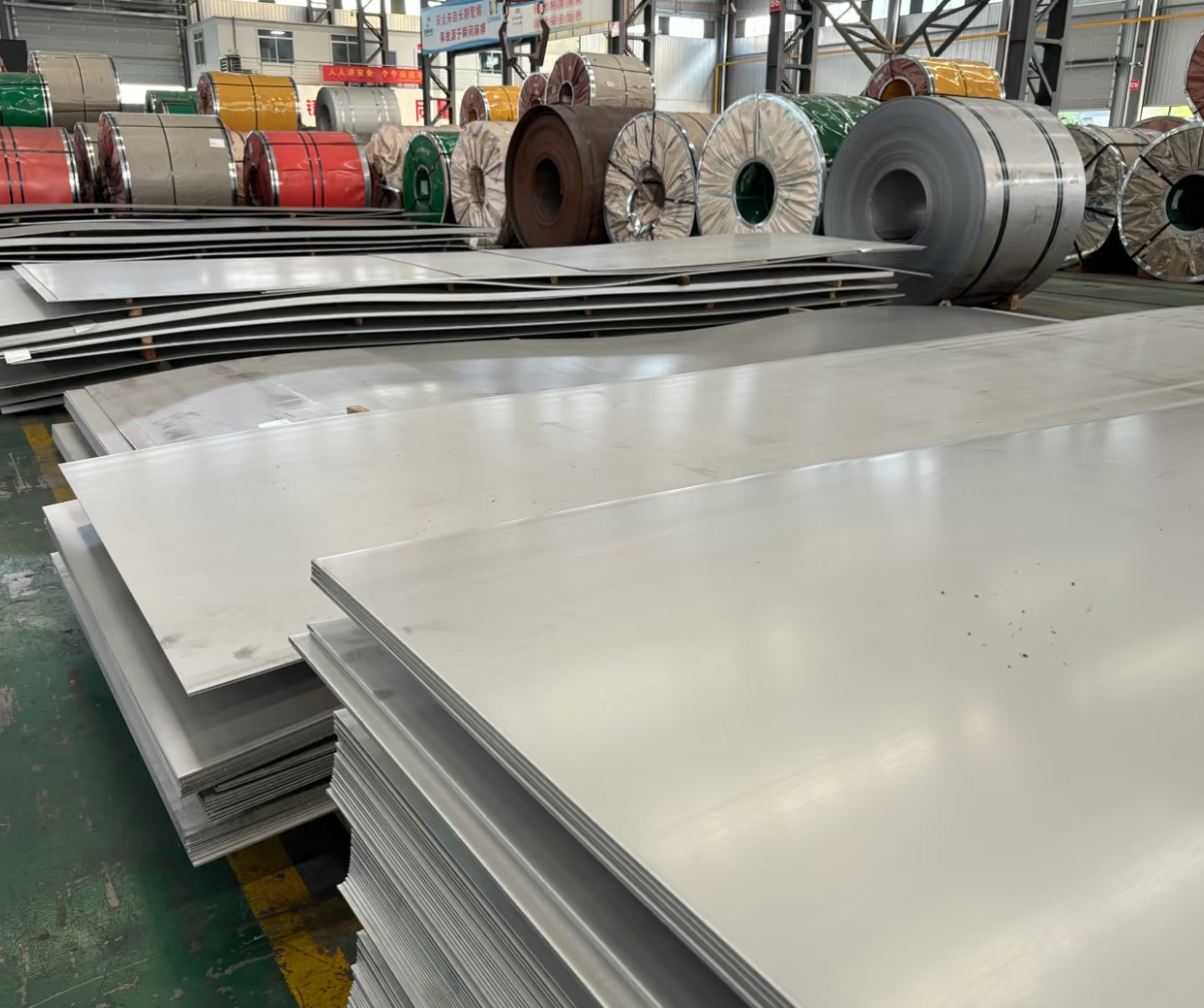

Stainless steel plates have several advantages, making them widely used in many fields:
Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to acid, alkali, and salt erosion, commonly used in high-temperature applications.
High-temperature Oxidation Resistance: Highly resistant to high-temperature oxidation, although the oxidation rate can be influenced by environmental factors.
Excellent Physical Properties: The metal's thermal conductivity determines its overall heat transfer coefficient, and stainless steel plates have better heat transfer coefficients than other metals with high thermal conductivity.
Aesthetic and Durable: With a smooth surface, easy to clean, durable, and aesthetically pleasing.
With the increase in downstream demand, the market demand for stainless steel products continues to rise, and inventory levels gradually decrease.
The global economic situation and the trends of other major economies also affect the stainless steel market in China. Changes in international demand and adjustments in trade policies may cause fluctuations in stainless steel prices and inventories.
Market Prospects:
Despite the current challenges facing the stainless steel market, its overall development prospects remain promising.
Manufacturing enterprises need to accelerate technological innovation and upgrades to production equipment to improve product quality and production efficiency, competing for market share.
Policy changes may bring new challenges or opportunities to the industry, and enterprises should closely monitor market dynamics and policy changes.
CREDIT
To ensure the quality of stainless steel plates, a rigorous quality inspection process is required. Here are some common quality inspection steps:
Rust Observation: Visually inspect the stainless steel plate surface for rust, including the distribution and color of rust spots, to initially assess its corrosion resistance.
Surface Quality Inspection: Check the stainless steel plate surface for scratches, pits, and other defects that may affect its corrosion resistance.
Spectroscopic Analysis: Use spectroscopic instruments to analyze the chemical composition of the stainless steel plate, detecting the content of key elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to ensure compliance with national or industry standards.
Mechanical Property Testing: Evaluate the mechanical properties of the stainless steel plate, including tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, to reflect its behavior under stress conditions.
Hardness Testing: Assess the wear resistance and compressive strength of the stainless steel plate through hardness testing.
Salt Spray Test: Conduct a salt spray test on the stainless steel plate under specific conditions to simulate its corrosion in marine environments or high-salinity environments, assessing its corrosion resistance.
In summary, as an important metallic material, stainless steel plates have a wide range of applications and significant advantages. With the continuous growth of market demand and technological advancements, their development prospects will become even broader. At the same time, rigorous quality inspection processes are required to ensure product quality.